Multi-player Graph Games
Strategic interactions on graphs for learning, control, and security
Many cyber-physical systems involve multiple agents that interact with each other and the environment in complex ways. The complexity of multi-agent systems grows exponentially with the number of agents, making traditional approaches computationally intractable. This project develops graph-mediated approaches that exploit the structure of agent interactions to enable efficient computation and scalable control.
Motivation
The control of complex multi-agent systems typically requires solving high-dimensional optimization problems over exponentially large action and state spaces. By leveraging the underlying graph structure of agent interactions—where nodes represent agents and edges represent direct interactions or dependencies—we can decompose complex problems into tractable subproblems and develop efficient algorithms for computing optimal strategies.
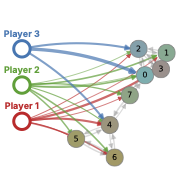
Social Influence Games
We study adversarial persuasion in social networks, where multiple competing players allocate limited budgets to influence individuals and shift collective opinions. Individual opinions evolve under DeGroot dynamics, and each player optimizes their influence allocation as a strategic player in a game.
Key results:
- Formulated as a difference-of-convex (DC) program enabling efficient solution
- Developed Iterated Linear (IL) solver that achieves solutions within 7% of nonlinear solvers while being 10x faster
- Scales to large social networks while maintaining interpretability through graph structure
By exploiting network structure, we efficiently compute equilibrium strategies that account for competing influences, providing a tractable and interpretable model of contested social influence.
See: Adversarial Social Influence: Modeling Persuasion in Contested Social Networks [1] (Accepted to ACC 2026)
Future Directions
Adaptive and Robust Strategies: Extend social influence games to develop strategies that are robust to perturbations in network structure and opponent behavior, enabling more resilient control in adversarial multi-agent settings.
Scalability to Complex Topologies: Study the impact of different network structures (scale-free, small-world, hierarchical) on the efficiency of influence strategies and the tractability of equilibrium computation.